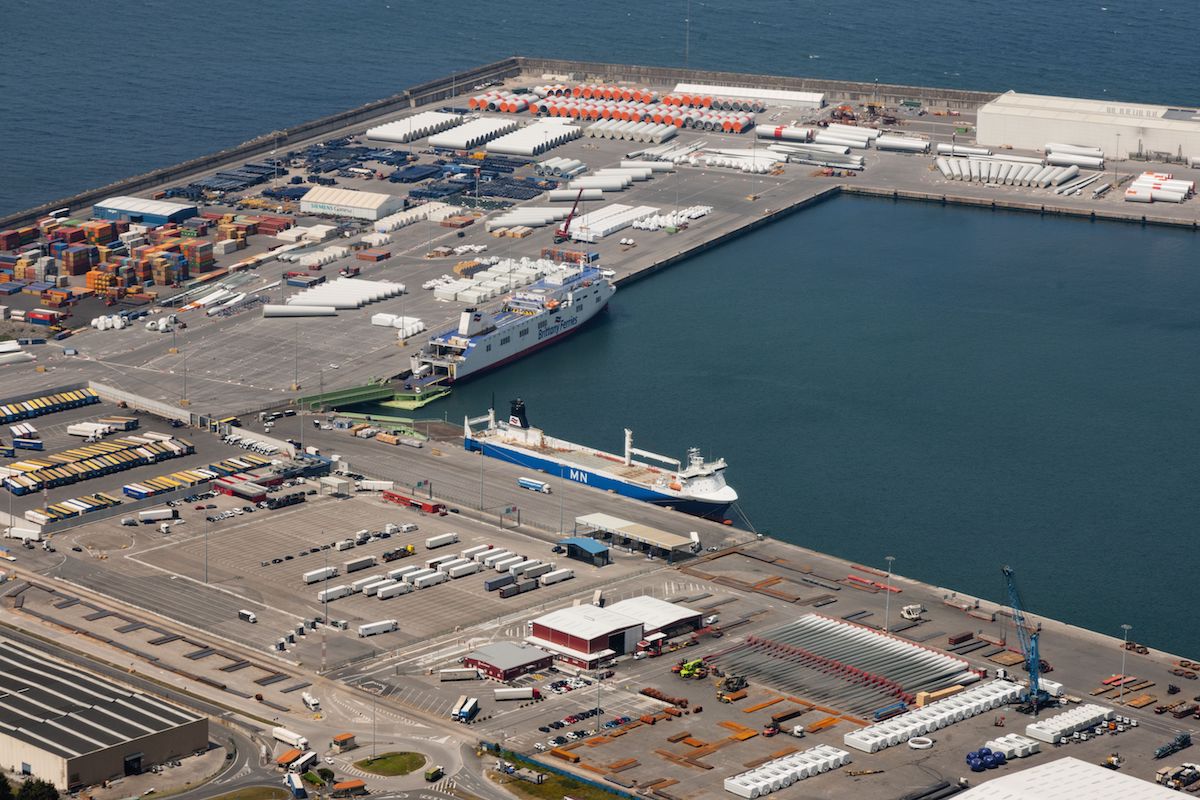
Repsol has started work on the construction of the LNG bunkering terminal in the port of Bilbao, from where the company will provide a bunkering service to the Salamanca and the Santoña, the two Brittany Ferries vessels due to come into service in 2022 and 2023 respectively.
The construction of this terminal is part of the long-term collaboration agreement signed in 2019 between Repsol and Brittany Ferries for the supply of LNG to their operations in Spain. The facility is scheduled to be commissioned in the first half of 2022.
The Bilbao terminal will be equipped with a cryogenic tank with a storage capacity of 1,000m³, making it possible for natural gas to be kept in a liquid state at -160ºC. The flexible design of the terminal will enable it to service different types of vessels in the future, thereby providing an important opportunity to decarbonise the port’s operations.
Thanks to efficient collaboration between Repsol’s engineering teams, the different public administrations involved and the Port Authority of Bilbao, the start of construction works has met the deadlines established in the agreement.
This project reflects Repsol’s clear commitment to industrial development and will involve an investment of over EUR 10 million, co-funded by the European Commission through the CEF – Connecting Europe Facilities – Programme. The construction of the Bilbao terminal is a further step towards the company’s goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2050, with a commitment to LNG as an alternative fuel for ships.
LNG in Spain
At present, Spain has 6 operational LNG reception and storage plants spread

along its coastline, from which the demand for this fuel can be supplied for the fleet of LNG vessels.
According to data from the Iberian Association of Natural Gas for Mobility (Gasnam), the number of LNG-powered ships worldwide currently stands at 221, a 70% increase compared to the 131 ships that were in operation in 2018.
LNG bunkering is an growing business with significant environmental benefits, as it reduces carbon dioxide emissions and reduces sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and particulate emissions to near-zero levels.

 Port access
Port access