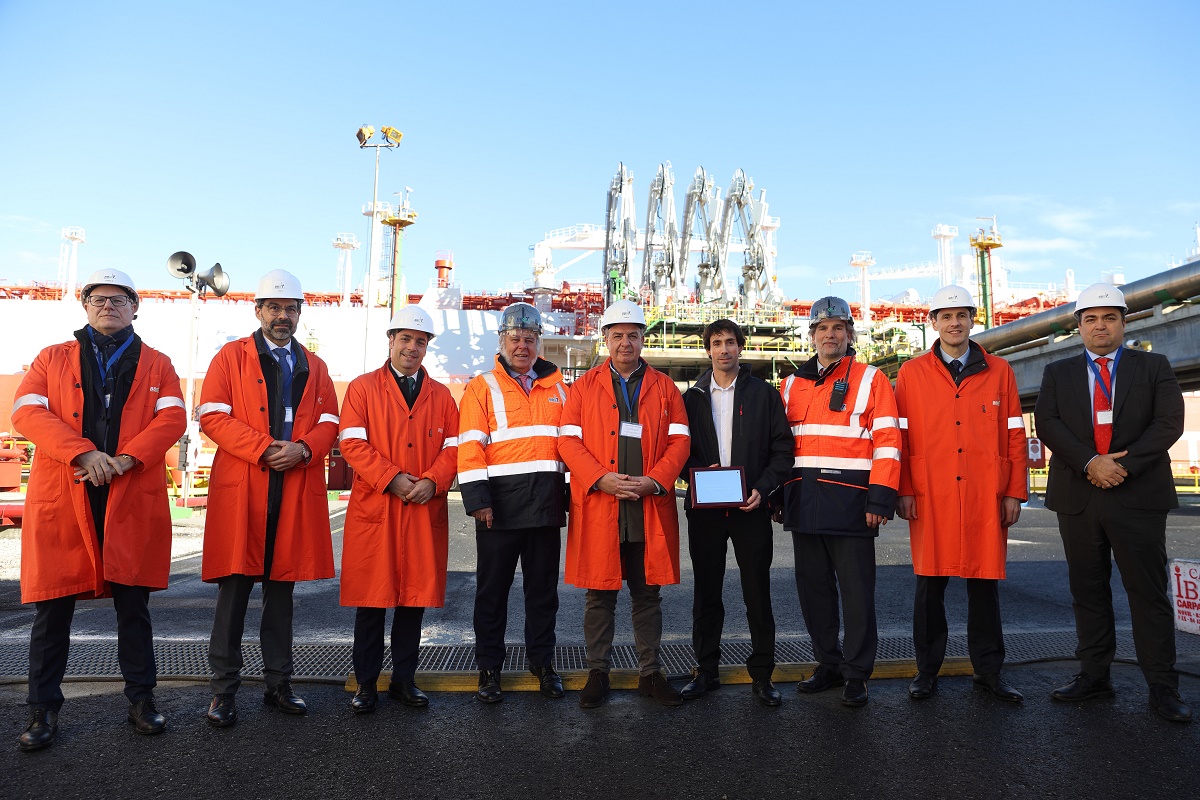
- The activity of BBG guarantees the supply of natural gas in the Atlantic Arc
- The plant covers 200% of the demand for gas in the Basque Country and 16% of the demand in Spain
- In 2024, gas consumption in the Basque Country amounted to 25,772 GWh
Bahía de Bizkaia Gas (BBG), the liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage and regasification plant located in the Port of Bilbao, has today welcomed the arrival of the methane tanker Rioja Knutsen, chartered by Naturgy, the thousandth such vessel to be serviced at this energy facility. This is a milestone for the most widely used plant in the Spanish gas system.
The Rioja Knutsen docked at the BBG jetty in the early hours of 20 January from the United States, and will remain there for 24 hours until the 164,000 m3 of LNG it is carrying have been unloaded. The vessel is an Atlantic Max 2G type LNG tanker, capable of transporting in its cryogenic holds liquefied gas maintained at a temperature of -163º C. Owned by Knutsen OAS Shipping, the tanker is 290 metres long, 46.4 metres wide, was built in 2016 in South Korea and sails under the Spanish flag.
Since the plant was commissioned in 2003, BBG has been of strategic importance for the entry of natural gas into the entire Atlantic Arc. Natural gas retailers that buy gas at source have opted for BBG due to the plant’s flexibility and capacity to accommodate increasingly efficient and larger vessels, such as the so-called Q-Max, the largest LNG carriers in the world capable of transporting up to 267,000 m3 of LNG in their holds. This traffic is also a key driver for the Port of Bilbao, accounting for over 10% of its total freight traffic.
The three BBG storage tanks, each one with a capacity of 150,000 m3 (the third tank was commissioned in 2015), provide a total storage capacity of 450,000 m3 of LNG. The regasification (returning the LNG to a gaseous state) capacity of the plant is 800,000 Nm3/h, and the gas is subsequently fed into the general supply network for consumption.
BBG system leader
BBG is co-owned by Ente Vasco de la Energía / The Basque Energy Agency, which was also the original promoter of the project, and the operator Enagás, both of which hold a 50% shareholding. In 2024, the plant welcomed a total of 49 methane tankers carrying 7.84 million cubic metres of LNG, equivalent to 3.4 million tonnes. In addition, BBG regasified a total of 50,887.4 GWh.
Last year, demand for natural gas fell by 4.2% in the whole of Spain compared to the previous year, mainly due to a 21.9% drop in gas demand for power generation. However, conventional demand increased by 3.1% compared to the previous year. In terms of natural gas supplies, 62% was supplied by LNG.
Within the gas system, BBG increased its share by receiving 27.24% of the total LNG entering the system, up from 22% the previous year. The plant also covered 200% of the demand for natural gas in the Basque Country and 16% of the demand for natural gas in Spain as a whole, thus achieving its primary mission of ensuring supply to the Basque Country and bolstering the Spanish gas system.
The BBG regasification facilities achieved the highest utilisation rate in the system, at 62.3%. Provisional financial results show an EBITDA of €23.3 million and net profits of €16.6 million.
Historic strategic project
The BBG LNG storage and regasification plant, one of the most ambitious and important energy projects developed in the recent history of the Basque Country, came into operation in 2003.
The project originated in the 1990s, at a time when industrial gasification in the Basque Country was well advanced but also faced supply shortfalls which needed to be addressed to meet the growing needs of the Basque production sector as a whole. Thus, BBG was conceived as a project to guarantee the supply of natural gas to the production sector and, at the same time, to transform the Basque Country into an important hub for connections to European gas networks. Today, BBG connects to the international market through maritime links with France and Europe via the Euskadour pipeline, and also links to Spain’s gas networks in the west and south.
Natural gas was introduced to the Basque Country 40 years ago to reduce reliance on petroleum products in its energy mix. Early gas networks replaced conventional fuels with this cleaner, more accessible energy source. Natural gas is the cleanest conventional energy source for electricity production, with CO₂ emissions 40-45% lower than coal and 20-30% lower than oil. Gas consumption in the Basque Country reached 25,772 GWh in 2024, 76% of which was for purposes of conventional consumption (industrial, household, etc.) and 24% for consumption in combined cycle power plants.
Over time, the use of coal in the Basque Country has practically disappeared and the use of oil derivatives in industry has been significantly reduced. Furthermore, and of particular importance for competitiveness, the uptake of natural gas has enabled far more efficient industrial technologies to be adopted, improving energy intensity and the competitiveness of Basque industry. The use of natural gas in the tertiary and domestic sectors has increased comfort and energy security for the entire population to unprecedented levels.

 Port access
Port access
